Welded Manufacturing
- Home
- Welded Manufacturing
WELDED PRODUCTION
What is Welded Manufacturing?
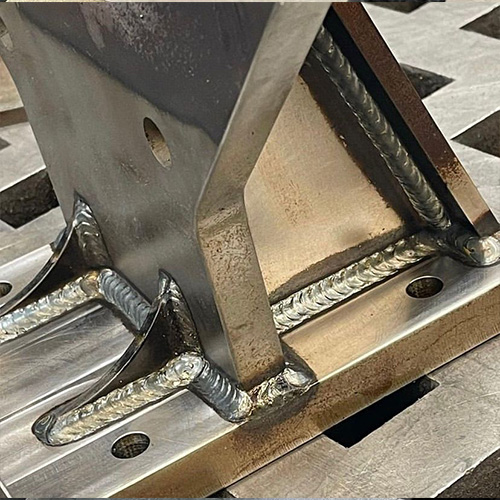
Welded manufacturing is a pivotal process in the construction and production of a vast array of products and structures. From the cars we drive to the bridges we cross, welding plays an essential role in building the modern world. This article delves into the intricacies of welded manufacturing, focusing on its significance, processes, types, advantages, challenges, and the role of metal welding within this sector.
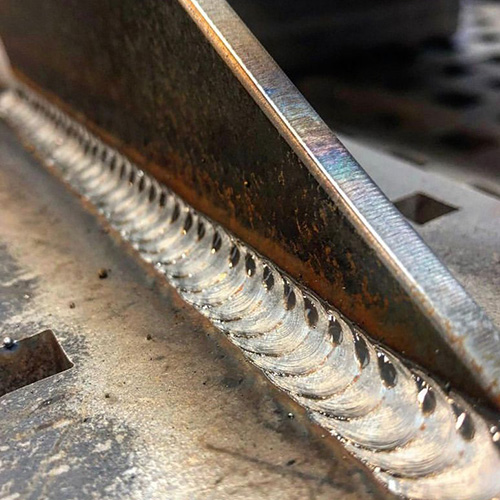
Welded manufacturing refers to the process of joining two or more pieces of metal or thermoplastics by applying heat, pressure, or both, creating a strong joint. This method is favored for its durability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, making it indispensable in various industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, and many more.
How to do Metal Welding?
Metal welding, a key component of welded manufacturing, involves the fusion of metals to form a strong bond. It is a skillful art that requires precision and knowledge of materials and techniques. The choice of welding method depends on the type of metals being joined, the specific requirements of the product, and the desired strength and appearance of the weld.
Types of Metal Welding Processes
There are several types of metal welding processes, each with its own set of advantages and applications:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Also known as stick welding, it is one of the most common forms of welding used in construction and repair work.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG): This method uses a wire feeding gun that feeds wire at an adjustable speed and sprays an argon-based shielding gas or a mix of argon and carbon dioxide over the weld puddle to keep it protected from contamination.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG): Known for its precision, GTAW is used when welding thin sections of stainless steel and non-ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys.
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW): This type combines the advantages of SMAW and GMAW, offering high welding speed and portability.
Advantages of Metal Welding in Manufacturing
Metal welding offers numerous benefits, including:
- Strength and Durability: Welded joints provide high strength, which is essential for structures that bear loads or undergo stress.
- Versatility: Welding can be used on a variety of metals and alloys, making it suitable for multiple applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Welding is often more economical than other joining methods, especially for large-scale manufacturing.
Welded manufacturing is a cornerstone of industrial production, enabling the creation of durable, high-quality products. With the continuous evolution of welding technologies and processes, the sector is set to meet the challenges of the future, further enhancing the capabilities and applications of metal welding. As industries strive for more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable manufacturing methods, the role of welding in shaping our world will undoubtedly continue to grow.